What Is The Data Rate For Hf Tags?
Contents
- What Are RFID Tags
- How Do UHF RFID Tags Piece of work?
- What's Within a UHF RFID Tag?
- Tag Form Factors
- Tag Positioning - SOAP
- Tag Attachment Methods
- Awarding Surface Materials
- Tag Special Features
- The Relationship Betwixt Tag Read Range & Size
What are RFID Tags?
RFID tags are placed on items to place or track those items over time or throughout their lifecycle. RFID tags tin can be used to rails all types of objects in industries like healthcare, retail, and manufacturing, to keep track of assets or inventory. This guide covers the main aspects to consider before deciding on or purchasing an RFID tag. Each tag may vary significantly from some other, which makes choosing ane that has been designed to work in environments and applications similar to your awarding essential in order to achieve the all-time results.
How Practise RFID Tags Work?
RFID tags communicate with RFID readers and antennas via electromagnetic waves. The reader/ antenna combination directs electromagnetic radio waves to the RFID tags in the vicinity. The energy from the waves, harnessed by the RFID tag's antenna, forms a electric current moving towards the center of the tag energizing the integrated circuit (IC). The IC turns on, modulates the free energy with data from its memory banks, and directs a signal back out through the tag's antenna. The remaining, modulated free energy that replies to the reader/antenna is known as "backscatter".
Quick Facts Most UHF RFID Tags:
- Well-nigh do non have a bombardment, and are powered exclusively past electromagnetic waves.
- Those with batteries (Battery-Assist Passive RFID Tags and Active RFID Tags) can achieve much longer read ranges.
- They do not crave line of sight, different barcodes.
- The fashion that tags couple, or talk to, the RFID reader is called "backscatter".
- An algorithm on each tag called "Anti-Collision" defines the order in which to reply if multiple tags are in the read area.
- The read range tin can vary from inches to over 120 feet depending on the tag.
- The integrated circuit (IC) has 4 memory banks – EPC, TID, User, Reserved.
- Each type of tag has a uniquely shaped antenna to ensure the best reactance.
What'south Inside a UHF RFID Tag?
A basic UHF RFID tag is comprised of an antenna and the IC.
Antenna – A tag'southward antenna is unique to that specific type of tag and its job is to receive RF waves, energize the IC, and and then backscatter the modulated energy to the RFID antenna.
Integrated Excursion (IC)/Scrap – the integrated excursion, also called the scrap, contains four memory banks, processing information, transport and receive information, and anti-collision protocols. Each IC type is unique, and there are only a handful of manufacturers. The principal variation betwixt ICs is the number of bits in the respective retentivity banks.
The four memory banks are as follows:
- EPC Memory Bank – contains the Electronic Product Lawmaking which tin can vary in length from 96 to 496 $.25. Some manufacturers apply a randomized, unique number, while others use random repeating numbers.
- User Memory Bank – the User memory bank tin can range from 32 bits to over 64k bits and is not included on every IC. If the tag does possess a User retentivity bank, it tin can be used for user defined data virtually the item. This could exist information like item type, terminal service date, or series number.
- Reserved Retentiveness Bank – the Reserved memory bank contains the access and lock passwords which enable the tag retentiveness to exist locked by the user and crave a password to view or edit.
- TID Memory Depository financial institution – the TID memory banking company contains the Tag Identifier which is a randomized, unique number that is ready past the manufacturer and cannot exist changed. In order for the reader to read this number instead of the EPC, the reader settings must be changed to accommodate.
Because there is a risk that a tag's EPC number is not unique, information technology is imperative to check before purchasing. Specifications may announce either "unique, randomized EPC number" or "Non guaranteed to be unique" (or some like phrase). If you purchase a tag without a unique randomized EPC number, it may need to be reencoded with a new, specific number. RFID readers are non able to differentiate between 2 tags that share the same EPC value.
The EPC number of each tag is read to identify the tag equally well equally the item that is tagged. If no software is used, the tag volition simply read the EPC number; simply, by incorporating software, it is possible to associate that number with a name, serial number, or even a picture on a database.
Tag Course Factors
Labels/Inlays
Labels and Inlays are two types of RFID tags that are characterized by being paper sparse and flexible. The main difference in labels vs. inlays is that inlays are typically clear and can be manufactured with or without agglutinative. Labels take a paper or poly (plastic) face then that that graphics or text can exist printed on them and read clearly
Usually grouped together because of form factor and cost, labels and inlays are cost effective and tin be purchased every bit depression as $0.10 per tag when purchased in higher quantities. These tags are manufactured on rolls of a few thousand and can be run through an RFID printer to be printed and encoded.
Labels and inlays usually weigh less than a gram and vary in length and width from about less than ½ an inch to over several inches.
Hard Tags
UHF RFID hard tags are classified as such considering they are rigid and thicker than the cardboard labels/inlays. Hard tags are made from many types of materials such as polycarbonate, ceramic, ABS, steel, polystyrene, and polypropylene.
Because of the tougher exterior and larger size, these tags are more expensive than labels and inlays. Depending on special features, difficult tags can range from only under $1 per tag to over $15 per tag. Just like labels and inlays, these tags can also be less expensive when purchased in higher quantities.
Hard tags vary profoundly in size and weight. The smallest tags are around 0.2 grams and the largest, rugged difficult tags can be over 250 grams. Shapes and sizes of hard tags vary greatly, and tin can range from the size of a small pencil eraser to as large every bit a license plate.
Tag Positioning - SOAP
Although tag positioning sounds like something to consider after a tag purchase, it is important at both the decision-making stage, too as the post-purchase phase.
The key to tag positioning is the acronym SOAP – which represents the 4 principal aspects of tag positioning – Size, Orientation, Angle, and Placement. Beneath is data about each, how to utilise them to select the ideal tag, and when to consider them.
Size
The size of the tag is an important consideration when purchasing. Not only does tag size matter considering it needs to fit the size of the object being tagged, just also because of the correlation between tag size and read range. In short, the larger the tag, the longer the read range (for more data, see The Relationship between Size and Read Range, page xiii).
Most Important: Pre-purchasing
Orientation
The tag's orientation, vertical or horizontal or otherwise, in relation to the RFID organization'due south antenna is a disquisitional gene in achieving ideal read rates. To find the orientation of the tag that produces the best read rates, rotate the tag on a flat surface and exam it at different orientations. Of note, using circularly polarized antennas helps to mitigate whatever issues acquired by tag orientation.
About Important: Pre-purchasing, Post-purchasing, Testing
Angle
The steeper the angle of the tag, the shorter the read range. When possible, ensure that the front of the tag directly faces the antenna. Fifty-fifty a small angle could cause a subtract in the tag's read range. To mitigate this event, it is all-time to an array of antennas to cover tags from multiple angles.
Pitch, Yaw, & Coil are three additional aspects to consider that fall under both orientation and angle. Testing to cover these positions, will ensure the best read range is received with the selected tag and system.
About Important: Mail-purchasing, Testing
Placement
Test readability in a diversity of spots on the particular to notice the "sweet spot" that generates the best reads. On a cardboard box for example, find the side that volition face the antenna/reader and and then exam in diverse places on that confront to find the one that produces the best results.
About Of import: Mail service-purchasing, Testing
Tag Attachment Methods
Dependent on the exact tag, attachment methods can vary from common forms like adhesive to unique ways such as shrink wrap. Inlays and labels use a permanent blazon of adhesive in most applications, while hard tags vary depending on the tag blazon, weight, application, and application environs. Below is a list of commonly used zipper methods for RFID tags.
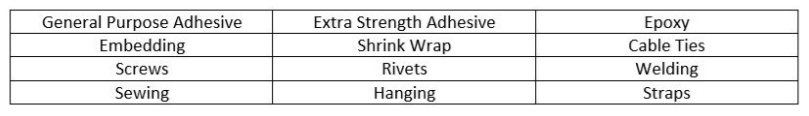
Deciding which attachment method to utilize volition depend on the tag, particular, and application. In all applications, choosing an attachment method tin can be only as important as choosing a tag. If an attachment method fails, the tag will fall off the detail making information technology no longer trackable, and the awarding no longer accurate.
Beneath are a few specific aspects to think near earlier choosing the right zipper method for your awarding.
Surface area – Just like prepping a car for a window or bumper sticker, the surface area of the item should exist prepped for the attachment of the tag. Depending on the method, make sure the surface is smooth, dust and h2o free, and make clean. (The tagging surface is further discussed in Awarding Surface Materials, page 09.)
Exposure – If the tag volition be exposed to prolonged UV light, moisture, vibration, pressure level, or chemicals, its attachment method will exist exposed as well. Certain environmental conditions like the ones listed above will demand special attachment methods that have been proven reliable in like circumstances.
Temperature – As mentioned above in the exposure section, brand sure that the attachment method chosen has been tested in similar weather as your tagging environment. Farthermost temperatures will take different furnishings on the compound or object used for attachment than the tag, like melting and/or becoming brittle and breaking.
Application Lifespan – Cull a tag besides as attachment method that volition concord up the length of time that the detail needs to be tagged. Some attachment methods volition slowly degrade over time, depending on the chemical makeup. Evaluate the attachment method called to ensure it can last the amount of time the tag needs to stay on the item.
Awarding Surface Materials
The surface of the particular to be tagged will profoundly influence tag option, and, if there is more than ane item surface type, a different tag should exist chosen for each. For instance, if an application is taking inventory of assets and one asset is metal and another is plastic, and so those two items will likely demand to exist tagged with two different RFID tags.
An object's surface textile is of import considering nearly tags have been tuned past the manufacturer to perform better when used on certain materials. The tag'southward antenna is very sensitive to the type of material it is placed on because of the way it sends and receives signals. Attaching a tag to an incompatible blazon of surface textile could issue in a lower read range, lower read rate, or no reading at all.
The near well-known surface material for crippling read range when tagged with the incorrect type of RFID tag is metal. Metal causes problems with RFID for two reasons – first, metal reflects RFID waves and, second, RFID tags are manufactured to perform on depression-dielectric surfaces (plastic, wood, cardboard) not high-dielectric surfaces like metal. There are ii easy ways to solve this issue, either purchase a metallic-mount tag that has a congenital-in, low-dielectric backing or is tuned accordingly, or purchase a tag and place a depression-dielectric textile such as foam, in between the tag and the metal object.
Tag Special Features
Nearly all UHF RFID tags accept special features that make them attractive to certain applications or environments. Most of the time, these special features will help narrow down the search for the ideal tag.
While labels/inlays only have a few feature options, hard tags take quite a few, which ordinarily explains their higher cost. Below are special features that tin exist institute on labels/inlays or hard tags, and information about how they are used.
- Resistance to extreme temperatures – Tags with this ability can exist used for tagging items in freezers or cold temperature environments (as low as -50° C), or with high-temperature environments (up to 250° C).
- Availability: Hard Tags
- Metal-mountable – A few label/inlays exist that are metal-mountable, but the majority of metal-mount RFID tags are hard tags. These tags are tuned to work well on metal and must be used when tagging metal items unless a spacer is used to separate the metallic object from the non-metallic mountable tag. Of annotation, tags made specifically for on-metallic applications tend to go better read range than those with spacers added postal service-manufacturing.
- Availability: Difficult Tags, All-Surface Label Tags
- Printability – The ability to print directly onto a tag's face is a unique feature of inlays/labels, which allows the tags to be identified visually, or support marketing/branding purposes. Virtually RFID inlays/labels can exist run through an RFID printer which is very user-friendly for large scale operations. Of note, while it isn't possible to print directly onto difficult RFID tags, most still are able to back up a manually practical label or sticker.
- Availability: Labels/Inlays
- Embeddability – The ability to be embedded within an detail is very useful in some rugged applications where the tag could potentially get knocked off or be in the way of the item's apply. Virtually embeddable applications involve wood or metal. The key to embedding tags in metal is to make sure that only 3 sides of the tag are covered with metal while one side is left open to allow for reader/tag advice. Epoxy can be used to cover the open side to seal the tag in identify.
- Availability: Difficult Tags
- Bear upon resistance – Some rugged application environments, like construction yards, need tags that tin withstand impact from other objects. Not-touch resistant hard tags will non exist able to withstand much shock before the enclosure breaks and the tag stops functioning.
- Availability: Hard Tags
- Vibration resistance – The vibration in vehicles, trains, and certain types of mechanism can be problematic for not simply RFID readers, but tags as well. Intense, constant vibrations demand to be mitigated by using a tag that tin stand up to that type of repetitive, high-intensity motion.
- Availability: Hard Tags
- Customizable – Most labels/inlays tin be customized with graphics, text, or colors, but other labels can be customized to a specific shape and form factor, material type, or given a specialty adhesive depending on the particular existence tagged. Some hard tags tin also be given a specialty adhesive, have labels manually applied, or exist produced in certain colors. A minimum order quantity commonly exists, only truly customizable tags can be designed and shaped according to the application'southward needs.
- Availability: Labels/Inlays, Hard Tags
- Autoclavable – The autoclave is a piece of machinery that is used frequently in the healthcare field to sterilize instruments after employ. Normal RFID tags cannot withstand the heat of the sterilization process, and so it is necessary to choose a tag that is autoclavable for these applications.
- Availability: Hard Tags
- UV resistance – In applications where the tagged item will spend a pregnant time subjected to UV (or Ultra-Violet) waves, if the tag contains printed information on its face, the called tag will need to be resistant to the UV exposure. This includes printed tags that will be unprotected from sunlight (through a window or door) for long periods of time.
- Availability: Hard Tags, Label Tags
- ATEX certified – ATEX certification means that the RFID tags are approved for use in environments with an explosive atmosphere. These tags are used for applications in environments similar mines or workplaces with activities that release flammable gases or vapors.
- Availability: Hard Tags
- Chemical Resistance – Chemic resistance is a feature that is used in the presence of airborne and water-based chemicals and then that the tag does not breakdown or corrode from exposure.
- Availability: Hard Tags
- Ingress Protection – For applications effectually dust/dirt or water, ingress protection ratings (or IP ratings) are incredibly of import to check before selecting a tag. The kickoff digit of the IP rating volition be 0 - vi and indicates the protection confronting solids like clay and dust. The second digit of the IP rating will be 0 – nine and is the level of protection against liquids, similar water. The highest IP ratings for tags would exist a rating of 67, 68, or 69 depending on direct or indirect contact with liquids.
- Availability: Hard Tags
- High Memory – Tags that are available with a higher User or EPC memory can exist used to store increased information on the tag, such as service dates and complete item identification. While high retention is skillful for some applications, nigh RFID systems associate the tag ID in a database containing the same information by way of software. This frees upwardly the memory on the tag and allows the tag to be read quicker.
- Availability: Hard Tags, Inlays/Labels
The Relationship Between Tag Read Range & Size
Ane of the biggest misconceptions nearly UHF RFID tags is that all tags get almost the same read range regardless of the size, materials, or tagged items. In truth, all those factors combine to determine a tag's full general read range, but the tag's size is the most influential component.
Because of how small antennas must be to fit within small tags, they can only send and receive data at simply a fraction of the distance of typical big tags. Some of the smallest UHF tags can just be read from a few inches away. Generally speaking, read range increases as the size of the tag increases, with some of the biggest passive tags being able to read over 35 meters (115 feet).
The correlation between read range and size suggests that, for each application, there must be a compromise between the ii in order to discover the platonic tag. In some applications, such as tool tracking, the objects to be tagged can be so small, that size isn't negotiable; therefore, tags for that application volition have just a short read distance. When tracking items that are more accommodating with regard to surface area – a medium to long range tag can be called and provide a improve balance between size and read range.
If yous take any additional questions about if RFID is right for your application, or about RFID tags, don't hesitate to contact us.
What Is The Data Rate For Hf Tags?,
Source: https://www.atlasrfidstore.com/what-are-uhf-rfid-tags/
Posted by: tsotherval.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is The Data Rate For Hf Tags?"
Post a Comment